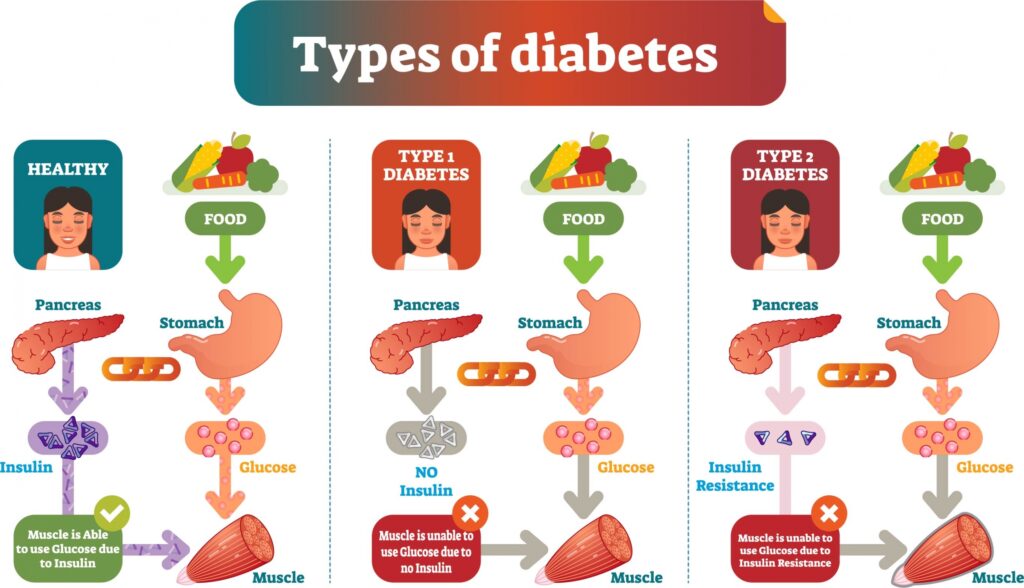
Diabetes is primarily divided into two types:
A) Type 1 Diabetes: This type is caused by the destruction of islet cells (most likely due to autoimmune processes, but also in chronic pancreatitis), leading to reduced insulin production. It usually occurs in patients between 4-14 years of age and is often associated with the development of other autoimmune diseases like hypothyroidism and celiac disease. Treatment involves insulin.
B) Type 2 Diabetes: This type is due to insulin resistance. The body initially tries to produce more insulin in response to raised blood sugar, but over time, the beta cells become fatigued and are unable to keep up with the increased blood sugar levels. It typically occurs in adults over 35 years of age. Treatment begins with oral hypoglycemic drugs and may progress to insulin therapy.
Apart from these two types, there are two other important types of diabetes:
C) Late-Onset Autoimmune Diabetes of Adults (LADA): This type involves the destruction of beta cells but occurs at an older age.
D) Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY): This type is characterized by increased insulin resistance in younger patients, usually in their 20s.
The treatment of LADA and MODY is similar to that of type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively.
