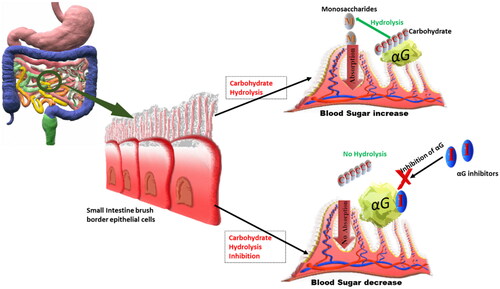
Carbohydrates are in the form of polysaccharides, formed of monosaccharides held together by alpha glucosidic bonds. Alpha glucosidase enzymes (brush border cells of intestine) break these bonds to release monosaccharides, and thus increase post-prandial sugar.
Alpha glucosidase inhibitors inhibit the conversion of polysaccharides into monosaccharides, and thus delay the rise in post prandial blood sugar.
1. Acarbose
- Brand names: Precose (in the U.S.), Glucobay (outside the U.S.)
- Dosage:
- Initial dose: 25 mg orally three times daily with the first bite of each meal.
- Maintenance dose: 50-100 mg three times daily, based on response and tolerance.
- Maximum dose: 100 mg three times daily (may be increased to 200 mg if necessary, but typically not recommended due to increased side effects).
2. Miglitol
- Brand name: Glyset
- Dosage:
- Initial dose: 25 mg orally three times daily with the first bite of each meal.
- Maintenance dose: 50 mg three times daily (may be increased to 100 mg three times daily depending on glycemic control).
- Maximum dose: 100 mg three times daily.
3) Voglibose is another alpha-glucosidase inhibitor used to manage postprandial hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is commonly used in parts of Asia, particularly India and Japan.
Dosage:
- Initial dose: 0.2 mg orally, three times daily before meals.
- Maintenance dose: 0.2 mg to 0.3 mg three times daily with meals, depending on the patient’s response and tolerance.
- Maximum dose: 0.3 mg three times daily.
Key Considerations:
- Common side effects: Flatulence, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, similar to other alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
- Contraindications: Patients with chronic gastrointestinal conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, ileus, or bowel obstructions.
- Monitoring
Key Considerations:
- Common side effects: Flatulence, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort (due to fermentation of undigested carbohydrates in the colon).
- Contraindications: Chronic intestinal diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, or conditions that may be worsened by increased gas.
- Monitoring: Blood glucose levels, especially postprandial glucose, and liver function tests for patients on acarbose.
